Introduction to Acrylic Rubber (ACM, AEM)-SKY RUBBER
Acrylic rubber ( ACM ) is copolymerized from acrylate monomers. Its main chain is a saturated carbon chain, and its side groups are polar ester groups. It has advantages such as simple processing equipment and ease of implementation.
Performance characteristics :
Advantages: It is heat-resistant, aging-resistant, oil-resistant, ozone-resistant, and UV-resistant. Its mechanical properties and processing properties are superior to fluororubber and silicone rubber, and its heat resistance, aging resistance, and oil resistance are superior to nitrile rubber.
Disadvantages: Not resistant to low temperatures, not resistant to water, relatively difficult to process, and not resistant to alkaline environments.

Main uses :
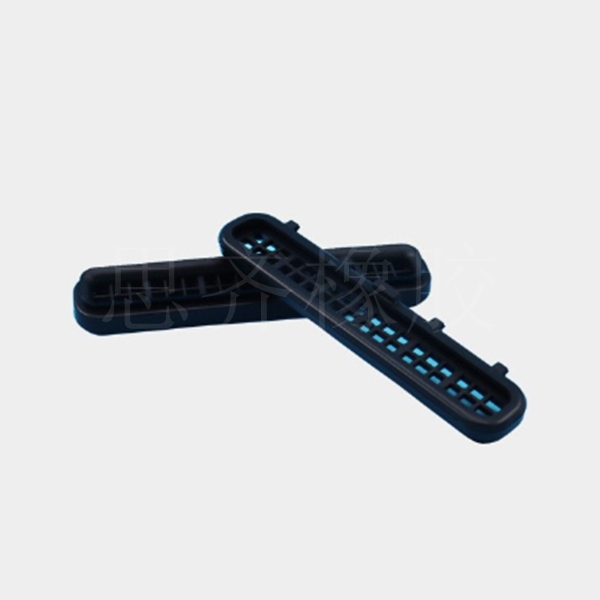
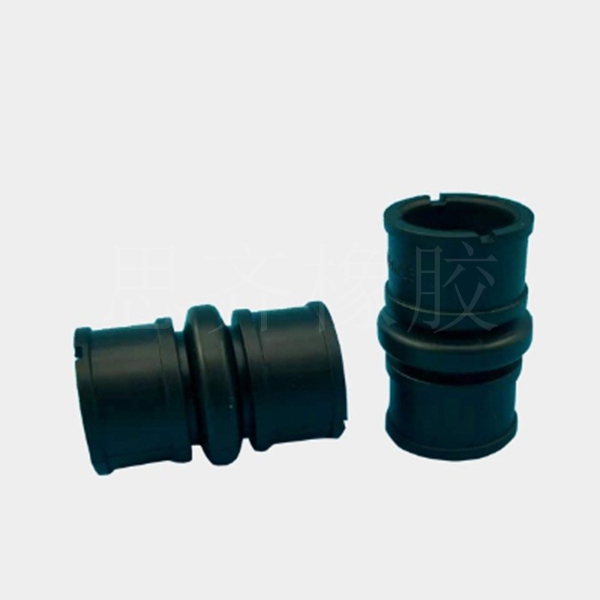
ACM is widely used in various high-temperature and oil-resistant environments, and has become a sealing material that the automotive industry has focused on developing and promoting in recent years, especially for high-temperature oil Seals, crankshafts, valve stems, cylinder head gaskets, hydraulic oil lines, etc.
Ethylene acrylate rubber ( AEM ) is a copolymer of ethylene, methyl acrylate, and carboxylic acid monomers. Its main chain is a saturated carbon chain, and its side groups are polar ester groups. It has the advantages of simple processing equipment and ease of implementation.
Performance characteristics :
Excellent heat aging resistance and liquid resistance; its heat resistance is superior to chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber ( CSM ) and NBR . AEM rubber has good resistance to ATF , gear oil, and ethylene glycol / water mixtures, but poor resistance to gasoline and phosphate ester hydraulic oils. Low oil swelling rate and high wear resistance.
Main uses :
Seals, gaskets, rocker arm cover seals, transmission oil cooling hoses, valves, dampers, shock absorbers; seals, sleeves, diaphragms, bellows, etc. for automotive powertrain systems.
| project | Performance characteristics | |
| ACM | AEM | |
| High temperature resistance | Maximum usable temperature for extended periods: approximately 180℃ | Maximum usable temperature for extended periods: approximately 180℃ |
| Low temperature resistance | Low-temperature brittleness temperature: -20 to -10℃ | Low-temperature brittleness temperature: -30 to -20℃ |
| Oil resistance | Both have comparable performance | |
| Processability | Poor machinability, prone to sticking to mold | Excellent processability |