Introduction to Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) -SKY RUBBER
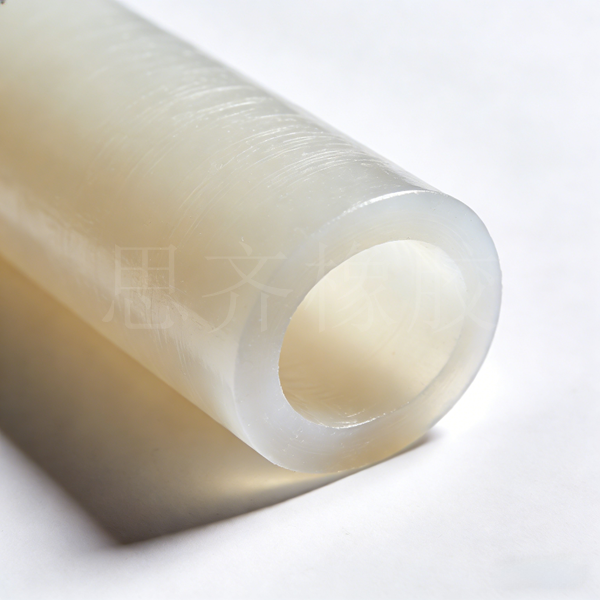
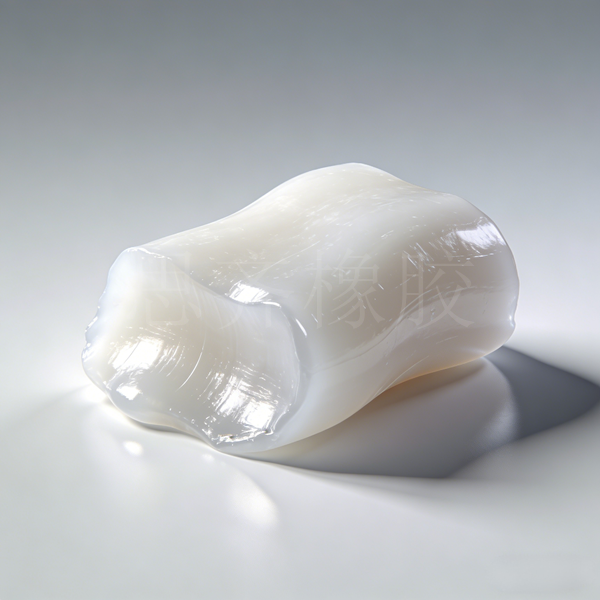
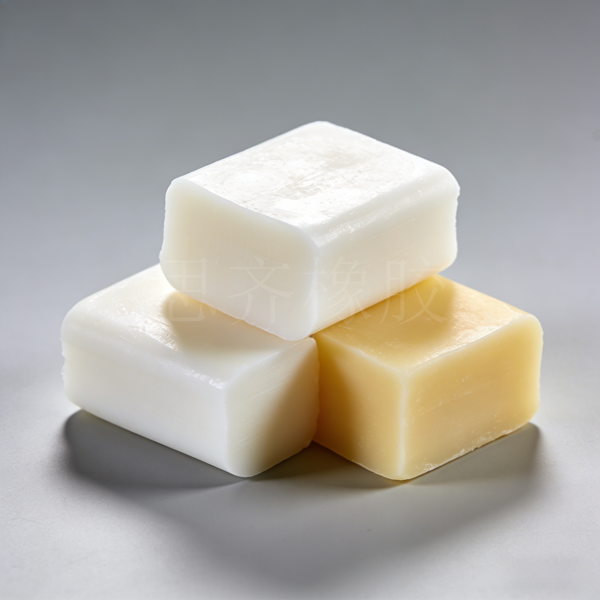
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a copolymer of styrene and butadiene. SBR can be classified into two types according to its polymerization method: emulsion polymerization and solution polymerization. The synthesis technology of emulsion-polymerized SBR was successfully developed by IGFarben in Germany in 1933. Solution-polymerized SBR was put into industrial production in the 1960s . It is estimated that in 2024 , the global SBR production capacity was approximately 6.817 million tons, accounting for about 30% of the total synthetic Rubber Production .
Performance characteristics :
Compared to natural rubber, styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) exhibits better heat resistance, aging resistance, and abrasion resistance. However, its elasticity, cold resistance, flexural crack resistance, and tear resistance are all inferior to those of natural rubber.
The higher the styrene content, the worse the elasticity, cold resistance, hysteresis loss, adhesion, and processing performance of styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR). SBR products generate a large amount of heat under repeated deformation, and this heat increases with the increase of the trans-structure content.

Main uses :
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a widely used general-purpose synthetic rubber with the highest consumption. It can be used in most applications except for those requiring special properties such as oil resistance, heat resistance, and resistance to special media.
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is mainly used in the tire industry. In the tire industry, SBR is widely used in passenger car tires, small tractor tires, and motorcycle tires, but less so in heavy-duty tires and radial tires.
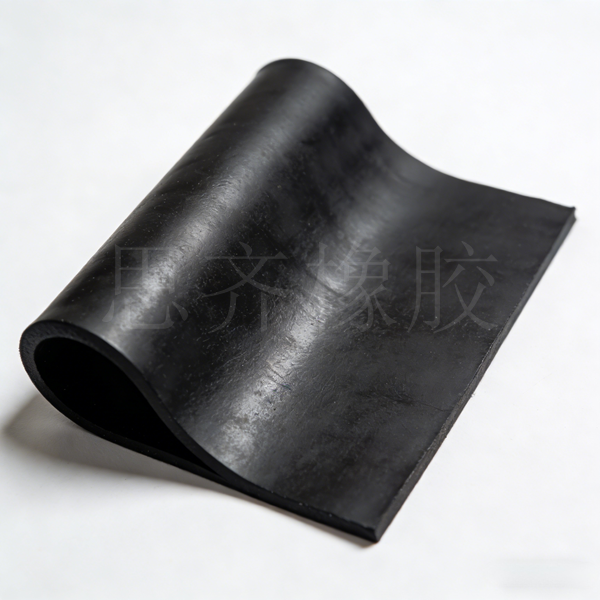
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) has also found wide application in conveyor belts, hoses, and some industrial products without special requirements. Examples include conveyor belt cover rubber, water hoses, rubber shoe soles, rubber rollers, waterproof Rubber Products, and rubberized fabrics.